AI and Water Consumption: An Unsustainable Use or a Recyclable Solution?

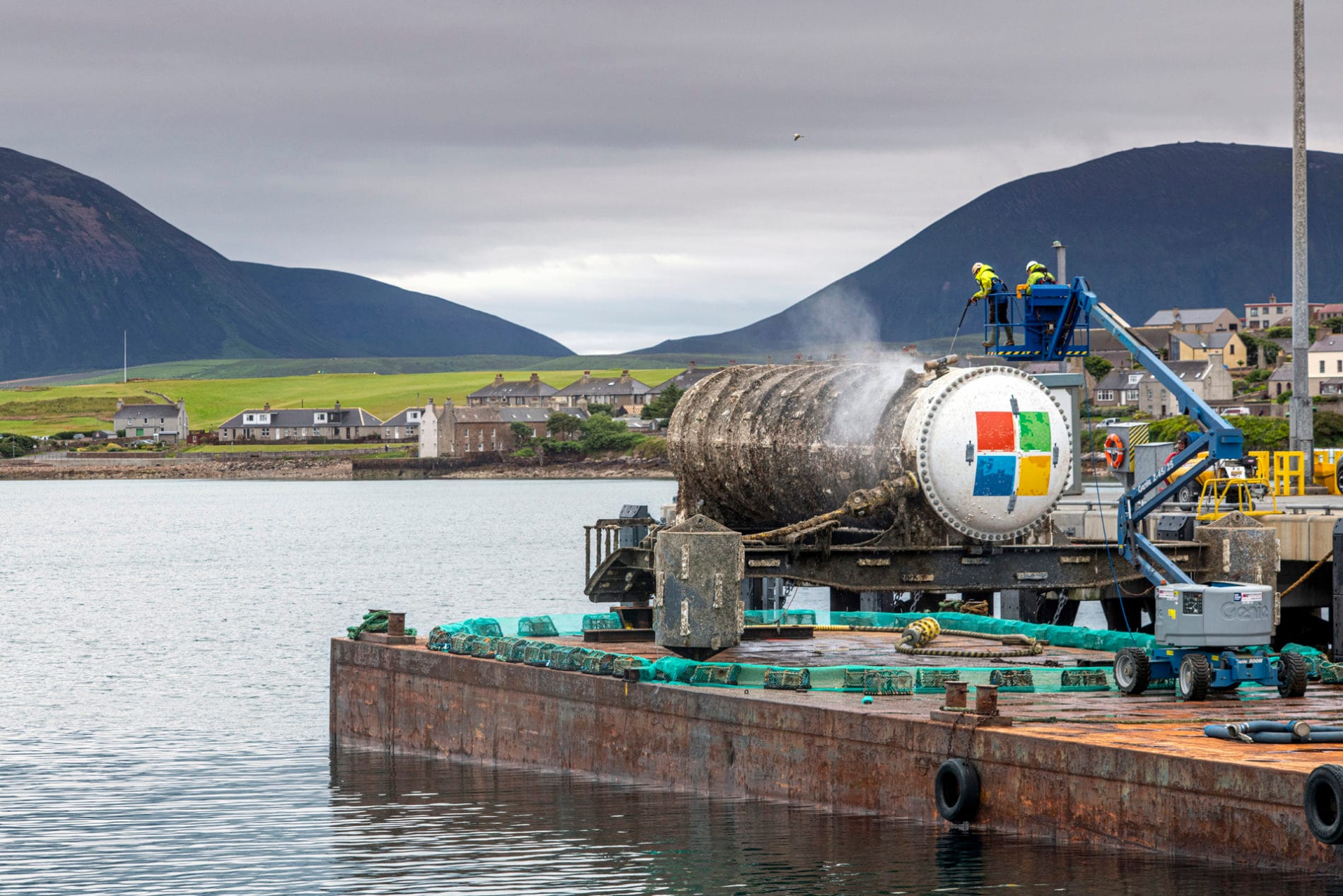
In the age of artificial intelligence, the consumption of natural resources is a growing concern. One often overlooked but significant aspect is the use of water in data centers that host AI servers. Despite the energy efficiency these centers aim for, water remains a crucial component for their operation. However, not all the water used is wasted. More and more companies are implementing technologies to reduce their ecological footprint, such as Microsoft’s Project Natick, a submarine data center that improves efficiency by eliminating the need for external cooling. The ocean itself cools the servers, thus eliminating the need for water consumption.

Water Recirculation: A Sustainable Solution?
While water usage in data centers raises concerns about sustainability, companies have begun implementing solutions to mitigate environmental impact. One of the most effective methods is water recirculation, a system where evaporated water is replaced by treated, recycled water.
Instead of relying on fresh water sources, companies are using recycled water or water from cooling towers, reducing consumption and minimizing environmental impact. In some cases, these recirculation systems are so efficient that a small amount of water can be used for months without the need for replenishment. However, challenges still exist regarding efficiency and scalability, making the sustainability of these systems dependent on local infrastructure and available technologies.
The water consumption associated with AI is concerning, but we must also recognize that water wastage is present throughout our environment.
Examples of Water Consumption:
- Shower:
- Average Consumption: An 8-minute shower can use between 60 and 100 liters of water.
- Waste: A long 15-minute shower could use over 150 liters of water.
- Washing Clothes:
- Average Consumption: A full load in a conventional washing machine consumes between 50 and 100 liters of water.
- Waste: Washing clothes unnecessarily (such as garments that are not dirty) contributes to significant water wastage.
- Industries:
- Textiles: The textile industry consumes approximately 10,000 to 20,000 liters of water to produce 1 kilogram of fabric.
- Food Industry: The food industry uses about 3,000 liters of water to produce 1 kilogram of meat.
While the water consumption associated with AI and data centers is undoubtedly a concern, it’s important to remember that any technological advancement, manufacturing process, or improvement inherently comes with an environmental cost. Whether it’s the production of electronics, the creation of infrastructure, or the development of new innovations, every step forward tends to require resources and energy, often leading to environmental impact.
However, this does not mean progress is inherently negative. The key lies in how we manage and mitigate these impacts. By developing sustainable technologies, implementing recycling systems, and optimizing resource usage, we can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of our advancements. In the end, the challenge is not to avoid environmental costs altogether, but to minimize them while continuing to innovate in ways that benefit society and the planet.



